NVIDIA debuted the new RTX 40 series in October with the release of the GeForce RTX 4090 24GB. In November, the GeForce RTX 4080 with 16GB was released. After a slight delay, probably due to the initial product names, we are finally looking at the GeForce RTX 4070 Ti 12GB. Now that we have three graphics cards from this line in our hands, we thought it was a great time to dive into their performance in various content creation processes, from 3D rendering to video editing. In this article, we'll take a look at their performance in Unreal Engine, with a focus on virtual production and game development.
In this article, we will use Unreal Engine to explore the performance of the GeForce RTX 40 series for real-time rendering. For comparison, we'll include the full lineup of the previous generation GeForce RTX 30 Series, the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, for additional context. We've also included a few offerings from AMD to see how they compare across different workflows.
General analysis of Unreal Engine performance
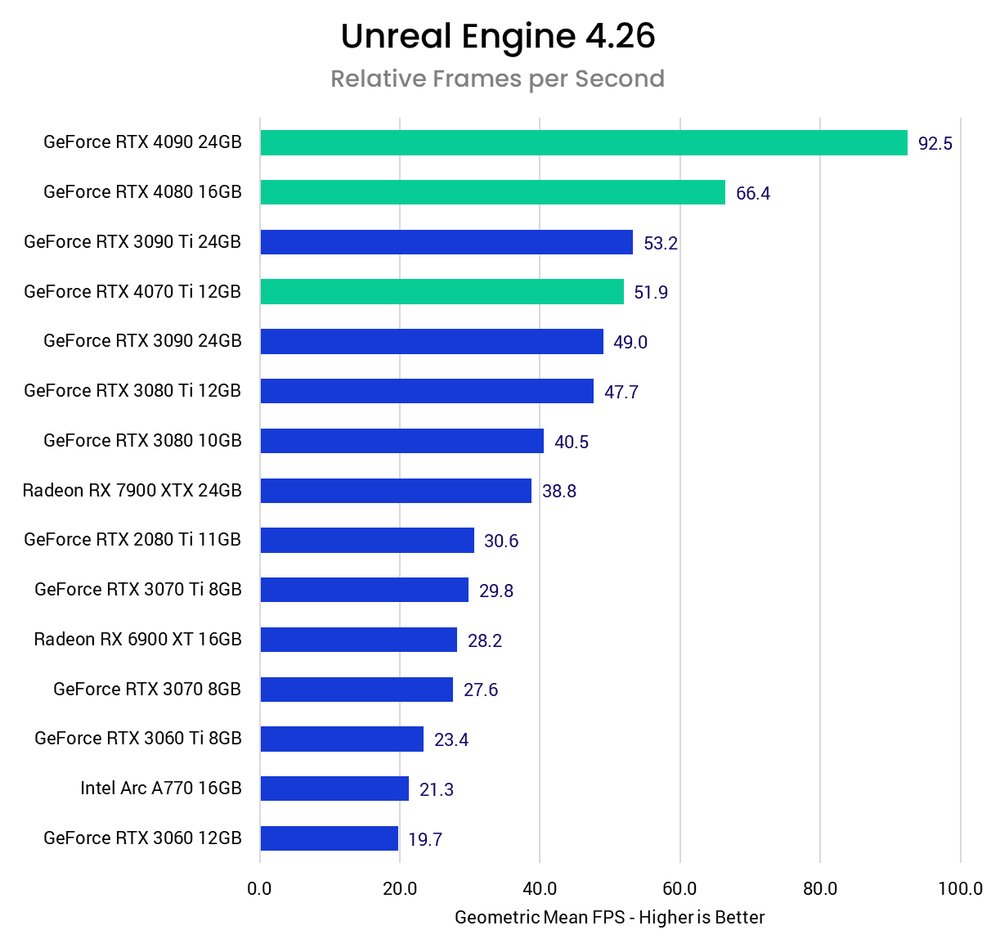
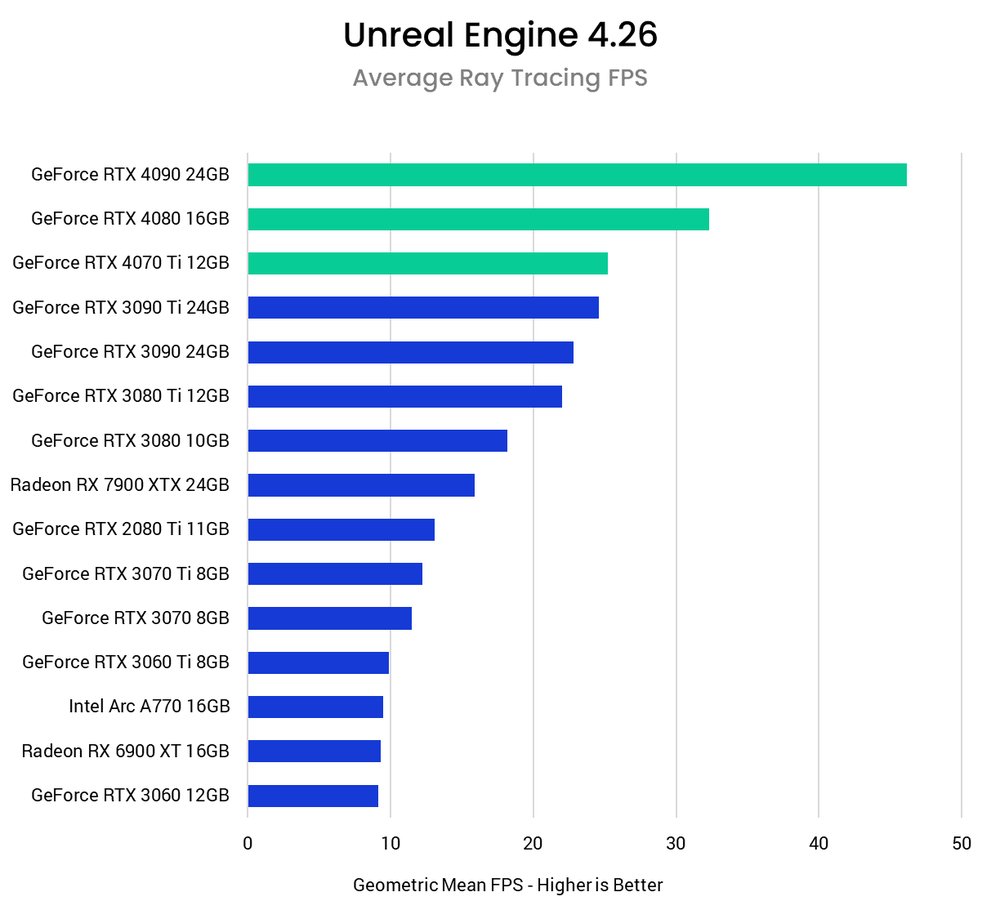
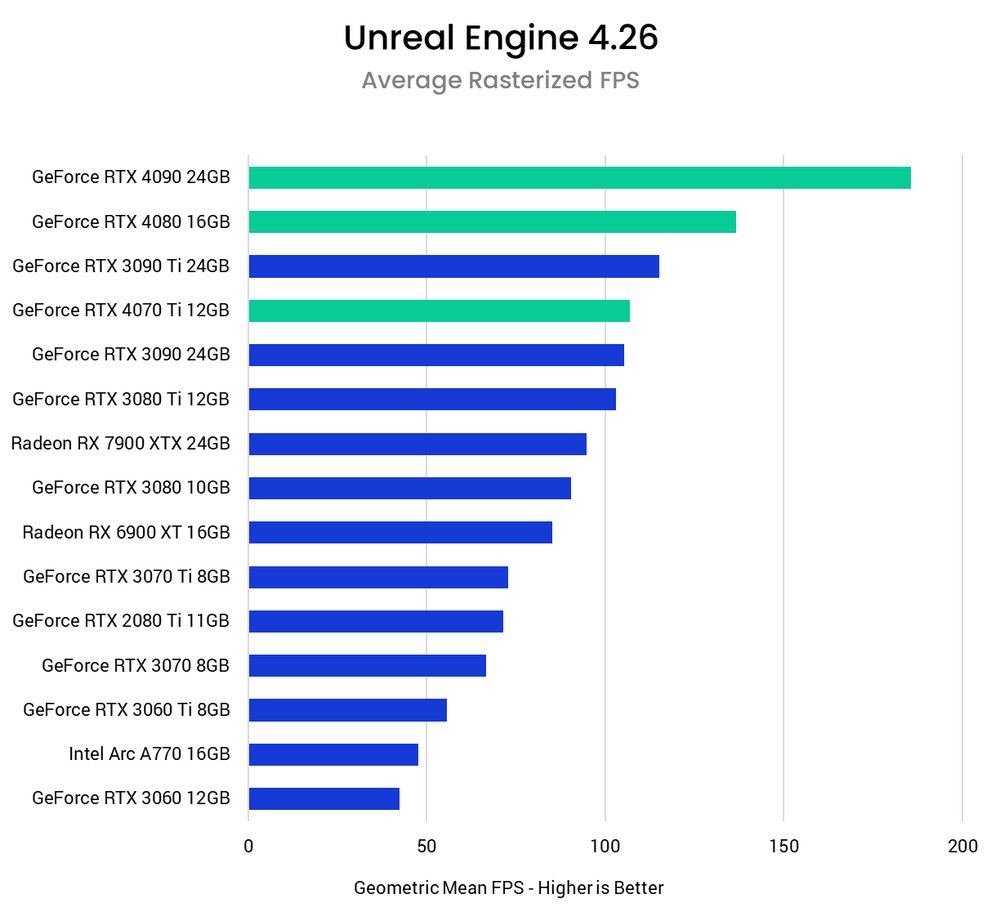
As we can see, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 series GPUs offer the highest potential frame rates in Unreal Engine. The newest release, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB, is almost as fast as the RTX 3090 Ti, often swapping places depending on the specific test scene, despite the price difference. At first glance, all three of the new RTX 40 series graphics cards seem to be great options for Unreal Engine development. Next, we'll take a look at these results to get more details on how they work together.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series vs. RTX 30 Series
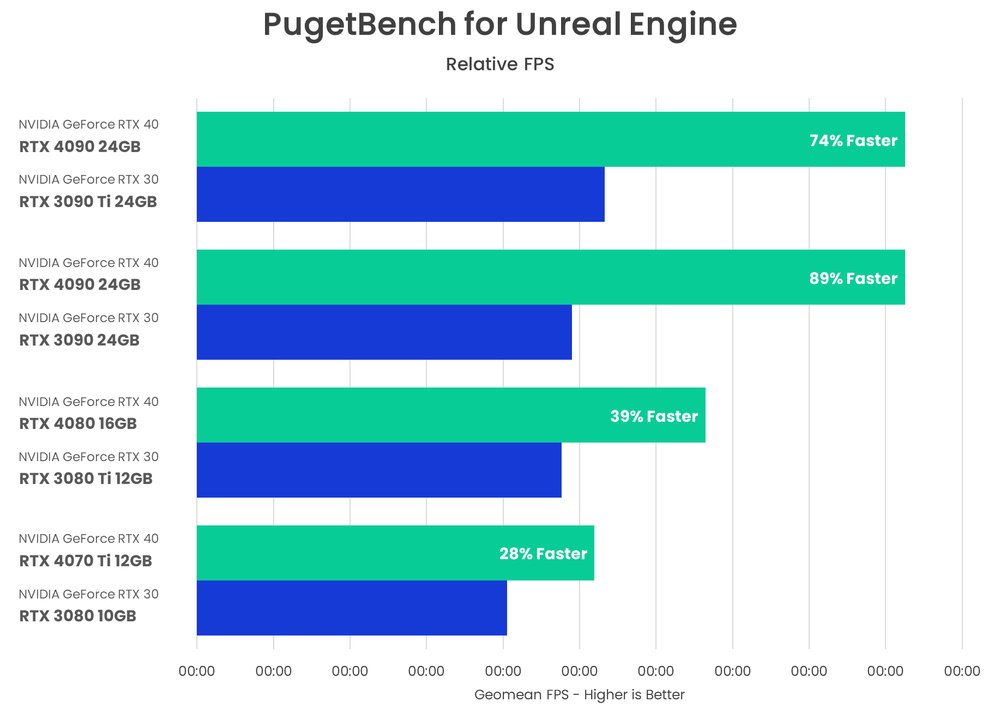
In the chart above, we compare the new generation of cards to their closest price equivalent in the previous generation. Due to changes in architecture, supply chain, etc., NVIDIA doesn't always keep their naming scheme consistent, so this gives you a better comparison of what performance you can expect for a given price. We've also added the top-end RTX 3090 Ti, although it doesn't have a price equivalent at the moment.
Starting with the RTX 4090 24GB, it delivers nearly 90% more frames than the RTX 3090, with only a 7% increase in price. For virtual production users, this means you'll be able to put a lot more geometry or effects on the screen while still maintaining your target FPS. It even outperforms the much more expensive RTX 3090 Ti, a GPU that is less than a year old. For those looking for the most productive GPU for rendering, the RTX 4090 with 24GB is definitely the best option.
Moving on to the RTX 4080 16GB, we note that this GPU costs the same as the RTX 3080 Ti, but delivers 39% more frames per second. It also increases the available VRAM from 12GB to 16GB, which allows you to render larger and more complex scenes. Again, this is a great improvement from generation to generation.
Finally, we'll take a look at the latest version, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB, which costs $100 more than the RTX 3080 10GB (about 14% more expensive). It delivers 28% higher FPS for that extra cost and has an additional 2GB of VRAM. While it is still a welcome upgrade over the RTX 3080, it is not as impressive as the RTX 4090 and 4080. If we compare by product name, the new RTX 4070 Ti is 74% faster than the RTX 3070 Ti, but it is also 33% more expensive. No matter how we compare, the RTX 4070 Ti delivers more performance than the increase in cost, but still not as impressive as its more powerful siblings.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series vs AMD Ryzen RX 7900 XTX
NVIDIA has long been the leader among GPUs in the Unreal Engine, although AMD has made huge strides in its performance in recent years and has become the one to watch in these professional workflows. As an “overall” assessment, it doesn't look good for AMD, but there are some big “asterisks” in these results. If we look at the results of specific benchmarks, we can see that in the first rasterized scene, the RX 7900 XTX performs very well, approaching the NVIDIA RTX 4080. This result is in line with some gaming benchmarks that can be found on the Internet. However, in the following rasterized scene, the 7900 XTX performs worse than the previous generation 6900 XTX. We have passed on our findings to AMD and they are looking into possible causes.
Let's move on to ray tracing workloads, which are a core workflow in virtual manufacturing. In this technology, NVIDIA has a generation-long advantage over AMD, and the benchmark results really show it. AMD is behind the 40-series, but close to the RTX 3080. While the RX 7900 XTX's 24GB of VRAM can be tempting, the ray tracing performance just isn't right for virtual production, but it can be a solid choice for game developers if you don't need to push the GPU to its limits.
How well does the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 work in Unreal Engine?
Overall, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 series offers a significant performance boost over the 30 series. The 24GB RTX 4090 is an outstanding solution, with 89% higher frame rates compared to the previous generation, while the 16GB RTX 4080 demonstrated a more modest 39% speed boost. The 12GB RTX 4070 Ti also shows improvement, although it is only 28% faster than the RTX 3080 at 14% higher MSRP. While not as impressive as the RTX 4090 or 4080, this performance increase puts it close to the performance of the RTX 3090 Ti.
Anyone working with Unreal Engine will appreciate the new NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 series. It not only brings better performance, but also additional VRAM for lower-end models. The biggest downside to these cards is the fact that the GeForce line has abandoned NVLink and still doesn't offer Sync support, so they may have limited use in high-end virtual production workflows. However, they are great for artist or game developer workstations.
Keep in mind that the test results in this article are for Unreal Engine only, and that performance will vary greatly from application to application. If your workflow involves other software packages, we highly recommend checking out our NVIDIA GeForce 40-Series vs AMD Radeon 7000 for Content Creation article, which includes results and links to in-depth testing for a number of other applications, including Premiere Pro, After Effects, DaVinci Resolve, Redshift, and Blender.